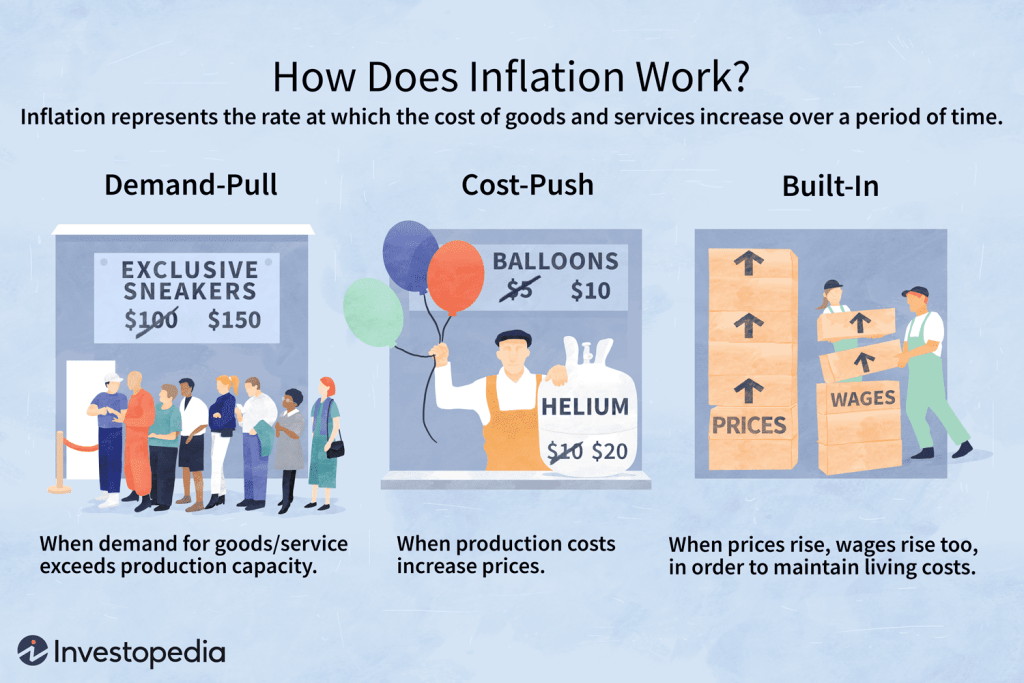
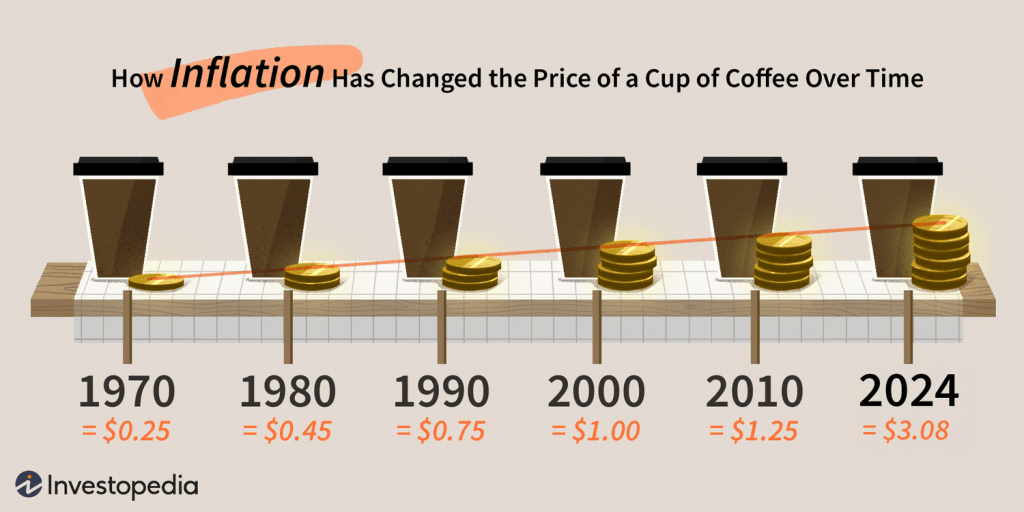
U.S. Inflation Outlook for 2025
By 2025, inflation in the U.S. is expected to continue its downward trajectory, though not likely to return to the Federal Reserve’s 2% target immediately. Analysts forecast that inflation will stabilize around 2.5% to 3% in 2025, driven by several key factors:
- Base Effects: A major reason for the expected moderation in inflation is that the high inflation rates of 2022 and 2023 will no longer be in the calculation base. This “base effect” means that even with moderate inflation, year-over-year comparisons will show lower inflation rates in 2025.
- Fed’s Tight Monetary Policy: The Federal Reserve’s monetary tightening from 2022-2024 will likely have a lingering effect on the economy. The higher interest rates that have been in place since 2022 are expected to dampen inflationary pressures by curbing demand for goods and services. These measures, however, come with a lag and might continue to cool the economy into 2025.
Factors Keeping Inflation Elevated
While inflation is expected to moderate, certain pressures could keep it above the Fed’s 2% target in 2025:
- Wage Growth: Labor market tightness is expected to persist into 2025, which could continue to drive up wages. The low unemployment rate and high demand for skilled workers could cause companies to increase wages to attract and retain talent. This wage-price spiral, if it continues, could put upward pressure on overall prices, especially in the services sector.
- Housing Market Costs: While the housing market may cool somewhat in 2024 due to higher mortgage rates, home prices and rents could still remain elevated in some parts of the U.S. Housing and rent are large components of the Consumer Price Index (CPI), and continued high costs in these areas could contribute to persistent inflationary pressures.
- Energy Prices: Although oil prices have been volatile over the past few years, any significant geopolitical instability (such as further disruptions in major oil-producing regions) or sudden supply chain bottlenecks could drive energy prices up again. If oil prices rise unexpectedly in 2025, this could push overall inflation higher.
Possibility of Economic Stagnation (Stagflation):
- Stagflation Risk: While unlikely, there’s a small chance the U.S. could experience a period of stagflation—a combination of stagnant economic growth and high inflation. This could occur if inflationary pressures remain high in essential goods (like food, housing, and energy), while economic growth stagnates due to restrictive monetary policy or external shocks.
Eurozone Inflation Outlook for 2025
In the Eurozone, inflation is expected to moderate in 2025, but similar risks to the U.S. could lead to prolonged price pressures.
- Expected Inflation: The European Central Bank (ECB) has been aggressive in raising interest rates in 2023 and 2024. By 2025, inflation in the Eurozone is expected to stabilize around 2% to 2.5%, assuming energy prices remain stable and economic growth picks up slightly after the global slowdown.
- Energy Dependency: Europe’s inflation outlook will heavily depend on energy prices, particularly natural gas. If energy prices remain volatile, inflation could exceed expectations in the short term. However, the shift toward renewable energy and better diversification of energy sources could mitigate these risks.
- Labor Market & Supply Chain Recovery: The European labor market has faced challenges with low workforce participation and an aging population. However, with increasing automation and digitization in certain sectors, the economy could become more productive by 2025, easing upward pressure on wages and prices. Additionally, ongoing supply chain normalization will likely help ease inflation in industrial goods.
Global Inflation Outlook for 2025
Moderate Global Inflation
Globally, inflation is expected to moderate by 2025. Global inflation was at historically high levels in 2022 and 2023, but much of that pressure has already eased in developed markets, and emerging markets are expected to follow suit. However, inflation dynamics may vary significantly by region.
- Emerging Markets: Inflation in many emerging markets (especially in countries like Turkey, Brazil, and Argentina) may remain volatile due to continued currency depreciation, political instability, and persistent supply chain disruptions. However, in markets with stronger fiscal and monetary policies, inflation could trend lower, potentially stabilizing in the 4%-5% range.
- China: In China, the economic slowdown combined with supply-side issues is expected to result in lower inflation in 2025. The People’s Bank of China (PBoC) may focus on stimulating domestic demand rather than combating inflation. Prices in key sectors like housing, food, and consumer goods could remain stable or experience moderate increases.
- Supply Chains: Global supply chains are expected to continue to improve in 2025, reducing the cost of raw materials, manufactured goods, and transportation. This will help to keep inflation in check in many economies, though certain industries (such as tech and energy) could still face price pressures.
Key Inflation Drivers to Watch in 2025
1. Central Bank Policies
While the Fed and other major central banks (ECB, BoE) are likely to ease monetary tightening in 2025, their policy decisions will still play a major role in shaping inflation outcomes. A shift toward rate cuts may stimulate demand but could also introduce new inflationary pressures, especially if economies rebound faster than expected.
2. Energy Prices & Geopolitical Events
Energy prices will remain a significant driver of inflation globally. Geopolitical instability, particularly in regions critical to oil and gas production (e.g., the Middle East, Russia, or Eastern Europe), could disrupt supply and push energy prices higher, reigniting inflation in developed economies.
3. Technological Advances
On the positive side, advances in automation, artificial intelligence, and green technologies could help drive down production costs, reduce reliance on expensive labor, and mitigate inflationary pressures in the long run. As these technologies continue to evolve, they could reduce the cost of goods and services in key industries.
4. Demographic Changes
In developed economies, the aging population is expected to limit workforce growth, which could keep wage pressures elevated. However, a potential shift toward automation and remote work could counteract these demographic pressures by boosting productivity without adding to inflation.
5. Global Trade Dynamics
Changes in global trade policies and globalization trends will influence inflation in various regions. While some countries might adopt more protectionist trade measures, others might push for further integration into global markets, which could help stabilize prices. However, global supply chain reconfigurations may take time, meaning inflationary pressures could persist in certain regions.
Conclusion: A Moderate but Uncertain Inflation Outlook for 2025
While inflation is expected to moderate in 2025 across much of the developed world, it is unlikely to return to pre-pandemic levels of 2% anytime soon. Central banks like the Fed may begin to lower interest rates in response to cooling inflation, but key factors like energy prices, wage pressures, and geopolitical risks will continue to influence inflation dynamics. The global economy faces both risks and opportunities in the fight against inflation, with some regions likely to experience more persistent price increases than others.
2025’s inflation outlook remains fluid, and policymakers will have to carefully balance growth and price stability as they navigate the economic landscape.